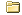
P
olar Bears Are Suffering from the Arcticís Loss of Sea Ice. So Is Scientistsí Ability to Study Them
The melting ice is affecting the bearsí behavior and physical condition, and it has made studying them through forays out onto the ice a treacherous business. . . .
Retreating sea ice in the Arctic is crippling scientistsí ability to study and monitor polar bears, Atwood and other experts say. The study of the bears, top-of-the-food-chain carnivores with adorable faces, is critical for conservation of the animals and their environment.
Studies show that the decline of sea ice, driven by climate change, is affecting the behavior and physical condition of polar bears, and making it harder for the animals to find enough food to survive. But fallout from global warming also means that Atwood and other researchers have fewer opportunities to hop in a helicopter for forays over the ice. Normally, polar bear scientists track the status of the bears by spotting them from an aircraft, sedating them and landing nearby to conduct a thorough biological examination.
The South Beaufort, where Atwood does his research, historically has been frozen over for most of the year, with some slivers of ice disappearing near the shores in late summer, usually August and September. But in recent years, the ice-free areas have greatly enlarged, and persisted for longer periods because of climate change. Over the last 25 years, the summer melt period has lengthened by as much as 82 percent, according to USGS studies, and sea ice cover has declined by more than half a million square miles.
The acceleration of sea ice melt results from a combination of warming Pacific Ocean water in the Bering Strait and record high surface air temperatures across the entire Arctic region, said Rick Thoman, a climate specialist with the Alaska Center for Climate Assessment and Policy at the University of Alaska, Fairbanks.
ďThe water and air temperatures are conspiring to not only reduce the extent of ice in all seasons but also leading to thinning of the ice that remains,Ē he said.
A couple of changes are that the polar bears are moving onto land and also that they are inbreeding more.

 Forum
Forum

 Home
Home 

 Album
Album 

 Help
Help

 Search
Search

 Recent
Recent 

 Rules
Rules 

 Login
Login

 Register
Register





 Pages: 1
Pages: 1